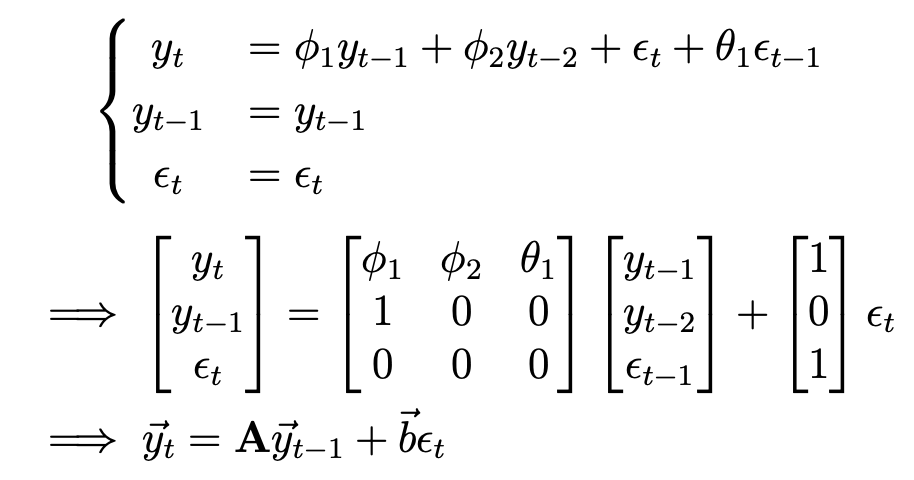벡터 자기회귀모델은 이전 포스팅에서 다루었던 자기회귀모델의 벡터꼴이다. 예시로 $VAR(1)$을 살펴보자. $$\begin{bmatrix} r_{t} \\ q_{t} \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} a & b \\ c & d \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} r_{t-1} \\ q_{t-1} \end{bmatrix} + \begin{bmatrix} \epsilon_{r,t} \\ \epsilon_{q,t} \end{bmatrix}$$ $$ \vec{x_{t}}=\textbf{A} \vec{x_{t-1}}+\vec{\epsilon_{t}}$$ 이전 포스팅에서 $AR(1)=MA(\infty)$로 쓸 수 있던 것처럼 벡터꼴의 자기회귀모델 또한 $VAR(1)$을 $V..